Welding injuries from insufficient PPE
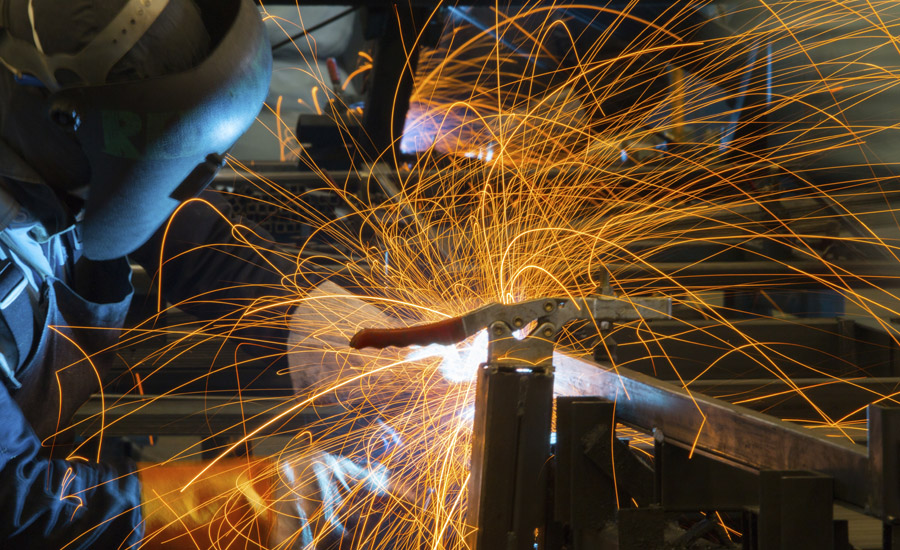

Personal protective equipment (PPE) helps keep welding operators free from injury, such as burns – the most common welding injury – and exposure to arc rays. The right PPE allows for freedom of movement while still providing adequate protection from welding hazards.
Thanks to their durability and fire resistance, leather and flame-resistant treated cotton clothing and newer flame-resistant fabrics are recommended in welding environments. This is because synthetic material such as polyester or rayon will melt when exposed to extreme heat. Welding leathers are especially recommended when welding out of position, such as applications that require vertical or overhead welding.
Avoid rolling up sleeves or pant cuffs, as sparks or hot metal will deposit in the folds and may burn through the material. Keep pants over the top of work boots – don’t tuck them in. Even when wearing a helmet, always wear safety glasses with side shields or goggles to prevent sparks or other debris from hitting the eyes. Leather boots with 6-to-8-inch ankle coverage are the best foot protection; metatarsal guards over the shoe laces can protect feet from falling objects and sparks.
Heavy, flame-resistant gloves should always be worn to protect from burns, cuts and scratches. As long as they are dry, they also should provide some protection from electric shock. Leather is a good choice for gloves.
Helmets with side shields are essential for protecting eyes and skin from exposure to arc rays. Make sure to choose the right shade lens for your process – use the helmet’s instructions to help select the right shade level. Begin with a darker filter lens and gradually change to a lighter shade until you have good visibility at the puddle and weld joint. The shade chosen should be comfortable and not irritate your eyes. Helmets also protect from sparks, heat and electric shock. Welder’s flash from improper eye protection may cause extreme discomfort, swelling or temporary blindness; don’t take any risks – wear a helmet at all times during welding.
To protect ears from noise, wear hearing protection if working in an area with high noise levels. This will also prevent metal and other debris from entering the ear canal. Choose ear plugs or ear muffs to protect the ears.
Other considerations For example, welders working in a confined space or in an elevated area make need to take extra precautions. In any welding situation, welding operators should pay close attention safety information on the products being used and the safety data sheets provided by the manufacturer, and work with their employer and co-workers to follow appropriate safe practices for their workplace.
If opening cans of electrode, keep hands away from sharp edges. Remove clutter and debris from the welding area to prevent tripping or falling. And never use broken or damaged equipment or PPE. To keep up with the most recent safety practices, welding operators should utilize resources from the American Welding Society (AWS), OSHA and welding manufacturers, such as Lincoln Electric’s online Interactive Safety Guide.
Source: Lincoln Electric http://www.lincolnelectric.com
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!