Arc flash hazards have not been adequately addressed in the mining industry
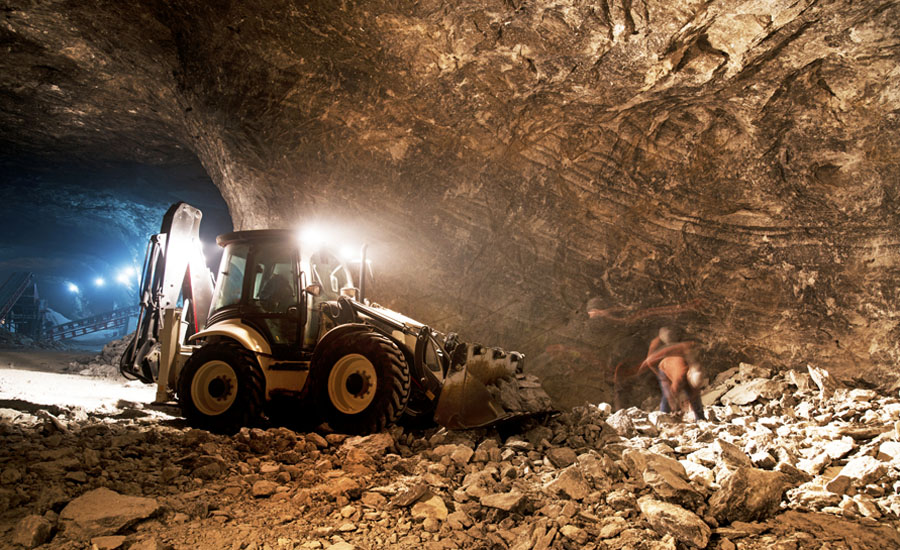

Arc flash generally refers to the dangerous exposure to thermal energy released by an arcing fault on an electrical power system. In recent years, arc flash hazards have become a prominent safety issue in many industries.
This problem, however, has not been effectively addressed in the mining industry. Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) data for the period 1990 through 2001 attribute 836 injuries to "noncontact electric arc burns," making them the most common cause of electrical injury in mining.
NIOSH published a paper presenting results from several elements of a recent NIOSH study of arc flash hazards in mining. It provides information and recommendations that can help reduce these injuries.
The characteristics of past arc flash injuries in mining are first outlined, such as the electrical components and work activities involved (based on MSHA data). This is followed by a review of important concepts and terminology needed to understand this hazard. Next, methods for identifying, measuring, and managing arc flash hazards on a power system are covered, with emphasis on recommendations found in NFPA 70E, Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace. Finally, results are presented from a detailed arc flash hazard analysis performed on a sample mine electrical power system using IEEE 1584-2004a, focusing on components and locations presenting severe hazards, as well as engineering solutions for reducing the risk to personnel.
Source: NIOSH
Looking for a reprint of this article?
From high-res PDFs to custom plaques, order your copy today!